Observatories and observations¶
Observatories glue together Atmosphere, Telescope
and Spectrograph properties as the base for
observations. They are callable with observing conditions (airmass,
seeing, moon brightness) and then create an “observation”.
There are two implementations of Observatory: The
SimpleObservatory uses a single spectrograph that can be
specified in the constructor, while the QMostObservatory
combines all three arms of a 4MOST “LRS” or “HRS” spectrograph, the
standard Paranal Atmosphere and the Vista telescope properties.
Observations can get a point like, flat, or sersic targets set, and then estimate the response to a specified exposure time.
See also
The class QMostETC provides the calculation of the
exposure time based on a specified ruleset.
- class qmostetc.SimpleObservatory(atmosphere, telescope, spectrograph, wl_range=None)¶
Object to put all components together for a simple observatory
This includes the atmosphere, the telescope, and one spectrograph. The object is callable; calling it with airmass, seeing, and moon brightness will create a new
SimpleObservation. The atmosphere is used only in the part relevant for the spectrograph.- Parameters:
- atmosphere
Atmosphere Atmospheric properties, for example
Atmosphere.paranal().- telescope
Telescope Telescope and fiber throughput, for example
Telescope.vista()- spectrograph
Spectrograph Spectrograph, may be f.e. built with
Spectrograph.qmost()- wl_range
astropy.units.Quantity Optional wavelength range [nm] to limit the detection range. If set to None (default), the original range of the spectrograph is used.
- atmosphere
Examples
This shows a complete observation of a template-generated point source:
>>> from qmostetc import SEDTemplate >>> observatory = SimpleObservatory(Atmosphere.paranal(), ... Telescope.vista(), ... Spectrograph.qmost('hrs', 'red')) >>> obs = observatory(45*u.deg, 1.3*u.arcsec, 'gray') >>> pck = SEDTemplate('Pickles_G0V') >>> flux = pck(15*u.ABmag, 'GAIA2r.G') >>> obs.set_target(flux, 'point') >>> tbl = obs.expose(300*u.s) >>> max_snr = (tbl['target'] / tbl['noise']).argmax() >>> print(f'Best SNR at {tbl[max_snr]["wavelength"]:.3f}' ... + f' (Signal: {tbl[max_snr]["target"]:.0f};' ... + f' Noise: {tbl[max_snr]["noise"]:.0f})') Best SNR at 650.772 nm (Signal: 153 electron; Noise: 14 electron)
- limit_wavelength(wl_range)¶
Create a new observatory with a limited wavelength
- Parameters:
- wl_range
astropy.units.Quantity Pair with (lower, upper) limits of the wavelength [nm]
- wl_range
- Returns:
SimpleObservatoryA new observatory with the limited wavelengths. If the paramter was None, the original
SimpleObservatoryobject is returned.
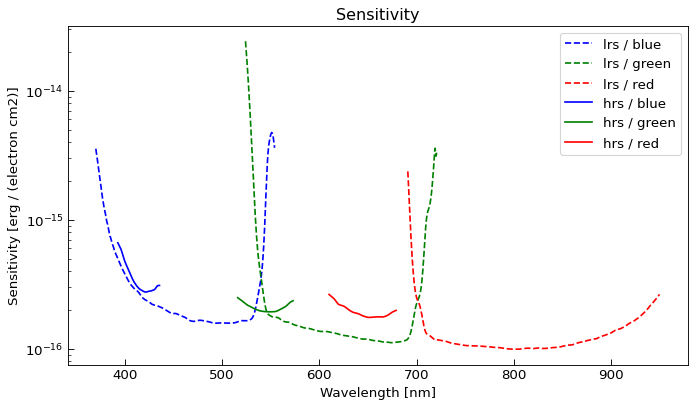
- property sensitivity¶
Return the sensitivity function
This function is created from
the spectrograph sensitivity,
the spectrograph binwidth,
the telescope throughput,
the telescope area
It converts the photoelectron counts into the flux at the entrance of the telescope.
The values of the array correspond to the wavelenghths that can be retrieved with
wavelength().This plot shows the sensitivity that is used by default for the 4MOST spectrographs:
- Returns:
astropy.units.QuantitySensitivity factors [erg/(cm² electron)]
Examples
Give the sensitivity array for the blue arm:
>>> observatory = QMostObservatory('lrs') >>> observatory['blue'].sensitivity <Quantity [3.55434960e-15, ..., 3.61695626e-15] erg / (electron cm2)>
- __call__(airmass, seeing, moon_brightness=None)¶
Start a new observation
- Parameters:
- airmassfloat or
astropy.units.Quantity Airmass to use (default 1.0). The airmass may also be given as zenith angle [deg].
- seeing
astropy.units.Quantity Optical seeing as a single Quantity at zenith [deg].
- moon_brightness
strorastropy.units.Quantity Moon brightness. One of
'superbright','bright','gray'or'dark'. Alternatively, the moon-sun separation [deg] can be given directly here. If not specified here, the sky spectrum must be given later withSimpleObservation.set_moon_brightness()or withSimpleObservation.set_sky().
- airmassfloat or
- Returns:
SimpleObservationA new observation, to which a target can be set and the exposure time can be applied.
- class qmostetc.SimpleObservation(observatory, airmass, seeing, moon_brightness=None)¶
Set up an observation with certain ambient conditions and pointing
- Parameters:
- observatory
SimpleObservatory Observatory that cause this observation
- airmass
floatorastropy.units.Quantity Airmass to use (default 1.0). The airmass may also be given as zenith angle [deg].
- seeing
astropy.units.Quantity Optical seeing as a single Quantity at zenith [deg].
- moon_brightness
strorastropy.units.Quantity Moon brightness. One of
'superbright','bright','gray'or'dark'. Alternatively, the moon-sun separation [deg] can be given directly here. If not specified here, the sky spectrum must be given later withSimpleObservation.set_moon_brightness()or withSimpleObservation.set_sky().
- observatory
- Attributes:
- observatory
SimpleObservatory Observatory for this observation
- sky
astropy.units.Quantity Sky emission measured at the fiber [photon/(s m² nm)]. The corresponding wavelengths are in
Atmosphere.wavelength.- airmass
float Airmass
- seeing
astropy.units.Quantity Target seeing [deg]
- exposures
dictof (str,Exposure) Dictionary with the spectrograph (arm) name as key and the corresponding
Exposureas value.
- observatory
- set_moon_brightness(moon_brightness)¶
Set a new sky spectrum based on a moon brightness
- Parameters:
- moon_brightness
strorastropy.units.Quantity Moon brightness. One of
'superbright','bright','gray'or'dark'. Alternatively, the moon-sun separation [deg] can be given directly here.
- moon_brightness
- set_sky(sky)¶
Set the sky brackground
This is an alternative for
SimpleObservation.set_moon_brightness()to set the sky background.- Parameters:
- flux
Spectrum Photon flux of the sky [ph/(s cm² nm arcsec²].
- flux
- set_target(flux, target_shape, sersic_radius=None, sersic_index=None)¶
Set the target object
- Parameters:
- flux
Spectrum Photon flux of the target [ph/(s cm² nm) for point sources, and ph/(s cm² nm arcsec²) for extended sources].
- target_shape
str Target shape. One of ‘flat’, ‘point’, ‘sersic’.
- sersic_radius
astropy.units.Quantity Sersic effective radius (only for Sersic target shape) [arcsec].
- sersic_index
float Sersic index (only for Sersic target shape).
- flux
- expose(exptime, nexp=1, var=None)¶
Create the result for a defined exposure time
- Parameters:
- exptime
astropy.units.Quantity Exposure time [s]
- nexp
int Number of exposures. Defaults to 1.
- var
strorNone Requested column (default None). If this is used, only a single quantity array is returned containing just the values of this column. Allowed values:
target: Target signal count [electron]sky: Sky background count [electron]noise: Noise count [electron]bg_noise_flux: Background noise flux [electron/s]snr: Signal to noise ratio
- exptime
- Returns:
astropy.table.QTable(if no columns were specified)Resulting table with the following columns:
wavelength: Left borders of wavelenght bins [nm]
binwidth: Wavelength bin width [nm]
efficiency: Spectrograph efficiency [electron/photon]
gain: Spectrograph gain [electron/adu]
target: Target signal count [electron]
sky: Sky background count [electron]
dark: CCD dark current [electron]
ron: CCD readout noise [electron]
noise: Noise count [electron]
astropy.units.Quantity(if a specific column was specified)Resulting array for the requested column
- property wavelength¶
astropy.units.Quantity: Left borders of wavelenght bins [nm]
- class qmostetc.QMostObservatory(spectrograph, spectral_binning=1)¶
Object to put all components together for 4MOST
This includes the atmosphere, the telescope, and the spectrograph. The object is callable; calling it with airmass, seeing, and moon brightness will create a new
QMostObservation.- Parameters:
Examples
This shows a complete observation of a template-generated point source:
>>> from qmostetc import SEDTemplate >>> observatory = QMostObservatory('hrs') >>> obs = observatory(45*u.deg, 1.3*u.arcsec, 'gray') >>> pck = SEDTemplate('Pickles_G0V') >>> flux = pck(15*u.ABmag, 'GAIA2r.G') >>> obs.set_target(flux, 'point') >>> tbl = obs.expose(300*u.s) >>> max_snr = (tbl['target'] / tbl['noise']).argmax() >>> print(f'Best SNR at {tbl[max_snr]["arm"]} arm,' ... + f' {tbl[max_snr]["wavelength"]:.3f}' ... + f' (Signal: {tbl[max_snr]["target"]:.0f};' ... + f' Noise: {tbl[max_snr]["noise"]:.0f})') Best SNR at red arm, 650.772 nm (Signal: 153 electron; Noise: 14 electron)
Similarly, this is a complete observation for a template-generated flat source:
>>> from qmostetc import SEDTemplate >>> observatory = QMostObservatory('lrs') >>> obs = observatory(45*u.deg, 1.3*u.arcsec, 'gray') >>> kin = SEDTemplate('Kinney_ell') >>> flux = kin(15*u.ABmag, 'GAIA2r.G') >>> flux = flux / u.arcsec**2 # The flat flux is per arcsec >>> obs.set_target(flux, 'flat') >>> tbl = obs.expose(300*u.s) >>> max_snr = (tbl['target'] / tbl['noise']).argmax() >>> print(f'Best SNR at {tbl[max_snr]["arm"]} arm,' ... + f' {tbl[max_snr]["wavelength"]:.3f}' ... + f' (Signal: {tbl[max_snr]["target"]:.0f};' ... + f' Noise: {tbl[max_snr]["noise"]:.0f})') Best SNR at red arm, 816.189 nm (Signal: 6350 electron; Noise: 80 electron)
- __call__(airmass, seeing, moon_brightness=None)¶
Start a new observation
- Parameters:
- airmass
floatorastropy.units.Quantity Airmass to use (default 1.0). The airmass may also be given as zenith angle [deg].
- seeing
astropy.units.Quantity Optical seeing as a single Quantity at zenith [deg].
- moon_brightness
strorastropy.units.Quantity Moon brightness. One of
'superbright','bright','gray'or'dark'. Alternatively, the moon-sun separation [deg] can be given directly here. If not specified here, the sky spectrum must be given later withQMostObservation.set_moon_brightness()or withQMostObservation.set_sky().
- airmass
- Returns:
QMostObservationA new observation, to which a target can be set and the exposure time can be applied.
- class qmostetc.QMostObservation(observatory, airmass, seeing, moon_brightness)¶
Set up an observation with certain ambient conditions and pointing
- Parameters:
- observatory
QMostObservatory Observatory that caused this observation
- airmass
floatorastropy.units.Quantity Airmass to use (default 1.0). The airmass may also be given as zenith angle [deg].
- seeing
astropy.units.Quantity Optical seeing as a single Quantity at zenith [deg].
- moon_brightnessstr or
astropy.units.Quantity Moon brightness. One of
'superbright','bright','gray'or'dark'. Alternatively, the moon-sun separation [deg] can be given directly here. If not specified here, the sky spectrum must be given later withQMostObservation.set_moon_brightness()or withQMostObservation.set_sky().
- observatory
- Attributes:
- observatory
QMostObservatory Observatory for this observation
- sky
astropy.units.Quantity Sky emission measured at the fiber [photon/(s m² nm)]. The corresponding wavelengths are in
Atmosphere.wavelength.- airmass
float Airmass
- seeing
astropy.units.Quantity Target seeing [deg]
- exposures
dictof (str,Exposure) Dictionary with the spectrograph (arm) name as key and the corresponding
Exposure) as value.
- observatory
- set_moon_brightness(moon_brightness)¶
Set a new sky spectrum based on the moon brightness
- Parameters:
- moon_brightness
strorastropy.units.Quantity Moon brightness. One of
'superbright','bright','gray'or'dark'. Alternatively, the moon-sun separation [deg] can be given directly here.
- moon_brightness
- set_sky(sky)¶
Set the sky brackground
This is an alternative for
QMostObservation.set_moon_brightness()to set the sky background.- Parameters:
- flux
Spectrum Photon flux of the sky [ph/(s cm² nm arcsec²].
- flux
- set_target(flux, target_shape, sersic_radius=None, sersic_index=None)¶
Set the target object
- Parameters:
- flux
Spectrum Photon flux of the target [ph/(s cm² nm) for point sources, and ph/(s cm² nm arcsec²) for extended sources].
- target_shape
str Target shape. One of ‘flat’, ‘point’, ‘sersic’.
- sersic_radius
astropy.units.Quantity Sersic effective radius (only for Sersic target shape) [arcsec].
- sersic_index
float Sersic index (only for Sersic target shape).
- flux
- property mean_loss¶
Return the mean atmospheric and telescope transmission loss
This is set by the
set_target()and can be used to calculate a kind of “fiber magnitude”.Note that this is very approximate, as it just averages the average transmission for each individual observation. It also just includes the atmospheric losses and the geometrical fiber fraction, no optical or other losses.
Examples
Calculate the fiber magnitude for a standard Pickles observation:
>>> from qmostetc import SEDTemplate >>> observatory = QMostObservatory('lrs') >>> obs = observatory(1.05, 0.8*u.arcsec, 'gray') >>> template = SEDTemplate('Kinney_s0') >>> mag = 20*u.ABmag >>> target_spectrum = template(mag, 'GAIA2r.G') >>> obs.set_target(target_spectrum, 'sersic', 1*u.arcsec, 1) >>> print(mag + u.Magnitude(obs.mean_loss*u.one)) 21.89... mag(AB)
- expose(exptime, nexp=1)¶
Create the result table for a defined exposure time
- Parameters:
- exptime
astropy.units.Quantity Exposure time [s]
- nexp
int Number of exposures. Defaults to 1.
- exptime
- Returns:
astropy.table.QTableResulting table with the following columns:
arm : Spectrograph arm (blue, green, or red)
wavelength: Left borders of wavelenght bins [nm]
binwidth: Wavelength bin width [nm]
efficiency: Spectrograph efficiency [electron/photon]
gain: Spectrograph gain [electron/adu]
target: Target signal count [electron]
sky: Sky background count [electron]
dark: CCD dark current [electron]
ron: CCD readout noise [electron]
noise: Noise count [electron]